Keyword
Geoscientific information
62 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
-
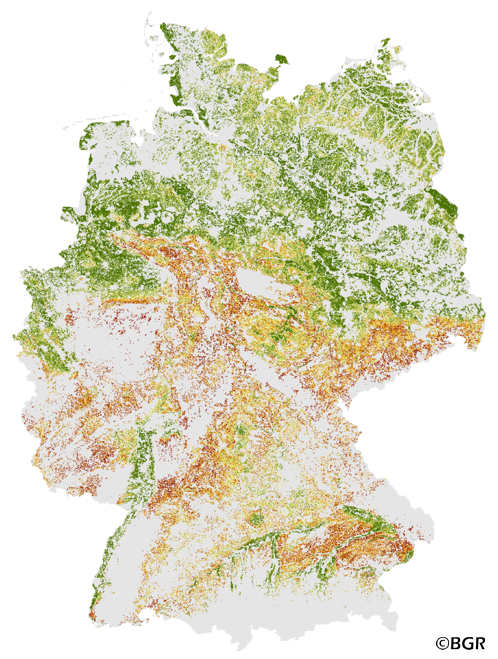
The Potential Soil Erosion Risk map gives an overview of the exposure of arable soils to soil loss due to surface runoff and splash erosion in Germany. It is based on pedological, relief and climatic factors. The map was created by using the long-term model USLE (Universal Soil Loss Equation). The method is published in the DIN 19708:2005-02 and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). For the application with soil maps, the method was adapted by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR).The landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 was used as pedological input to the model. The relief data was derived from the DEM50 of the BKG. The mean annual precipitation data of the period 1961-1990 (DWD) is used to model the erosivity of rainfall. The land use information is derived from CORINE land cover data set (2006).
-
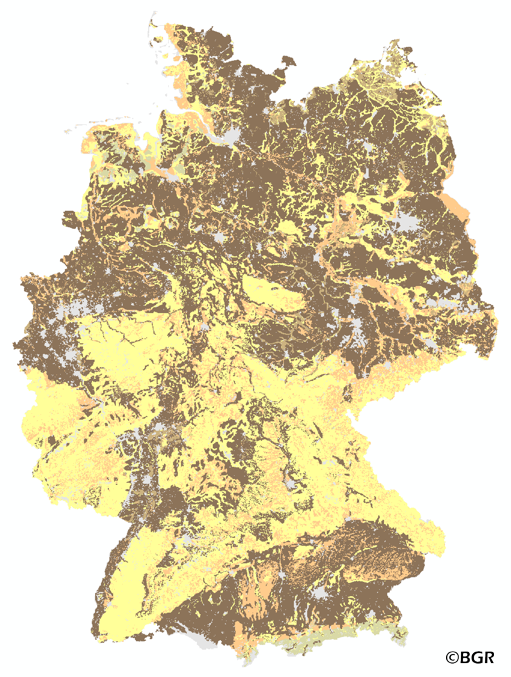
The map of the soil depth gives an overview of the rooting capacity of German soils. The soil depth is derived from profile data of the landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000. The lower limit of a soil is bedrock or a groundwater influenced horizon. The method is derived from Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung KA5 (2005) and is documented in the MethodenWIKI of the FISBo BGR. The land use information is derived from the CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-
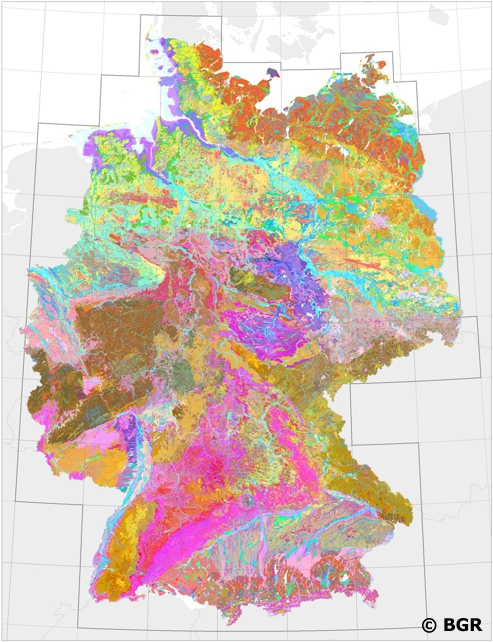
Nation-wide land use strategies and planning as well as soil protection require harmonised and standardised area-covering information. Such data is provided by the digital Soil Map of Germany at scale 1:200,000 (BUEK200). The pedological data of this map, stored in a relational database, is used to demonstrate the abundance and the associations of soils and their basic properties in Germany. However, the main purpose of the BUEK200 is to offer a database which allows the estimation and visualisation of soil functions, soil potentials and soil hazards. To achieve comparable soil information throughout Germany the BGR and the soil surveys of the federal lands have elaborated and defined BUEK200 standards concerning the map (e.g. delineation and description of mapping units) and its database (e.g. database model, parameters, codification).
-
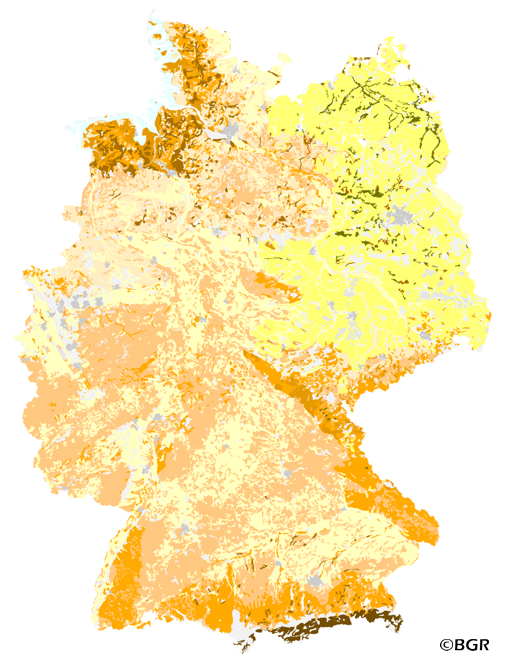
The map Organic Matter Content of Top-Soils in Germany 1:1,000,000 highlights the results of a Germany-wide compilation of typical soil organic matter contents in top-soils differentiated according to 15 groups of soil parent material, four climatic areas and the main land use. The evaluation is based on more than 9000 soil data profiles with information about Soil Organic Matter (SOM) from a period of about 20 years. The report 'The Organic Matter Content of Top-Soils in Germany', BGR Archiv, No. 0127036 (in German) documents the methodology. The classes of the map legend are based on the classes given in the German Soil Mapping Guideline, 5th Edition (KA5).
-
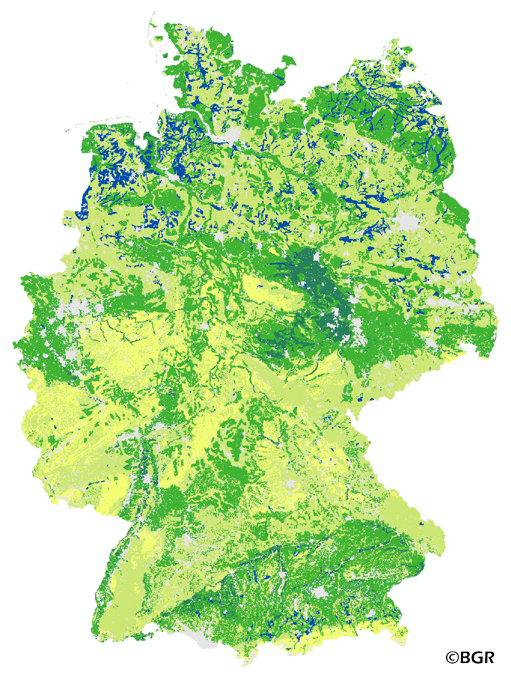
The map of the field capacity of soils in Germany gives an overview of the amount of water which can be stored in a soil (depth 1 m). The water storage capacity is a key function of soils. The field capacity was derived from the landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung KA4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is derived from the CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-
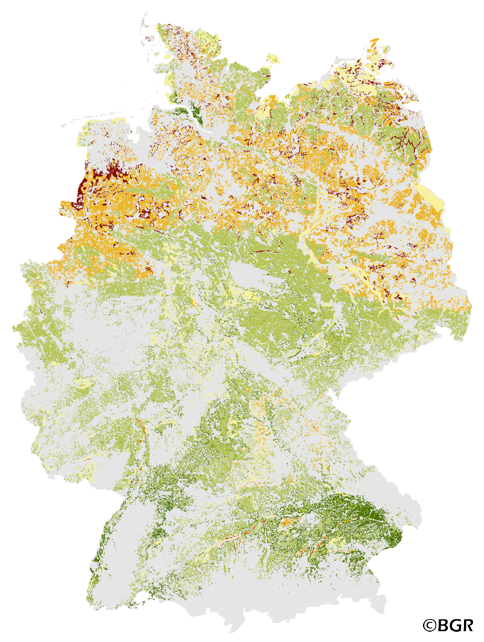
The Potential Wind Erosion Risk map gives an overview of the exposure of arable soils to soil loss due to deflation in Germany. It is based on pedological and climatic factors. The method to predict the soil erosion risk is published in the DIN 19706:2002 and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). For the application with soil maps, the method was adapted by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR).The land use stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 was used as pedological input to the model. The mean annual wind speed at 10 meters above ground level of the period 1980-2000 (DWD) is used as well. The land use information is derived from CORINE land cover data set (2006).
-
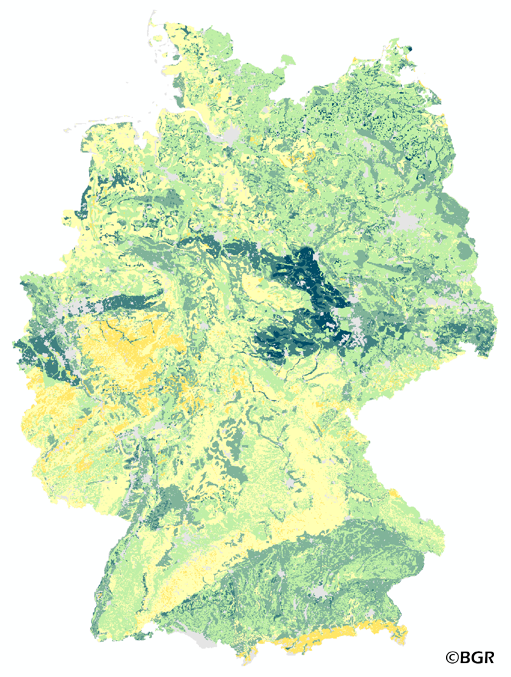
The map of the available water holding capacity in Germany gives an overview of the amount of water in a soil that is normally available for plant growth. The map shows the available water from the surface to effective rooting depth, which is derived from land use and soli data. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung KA4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is taken from the CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-
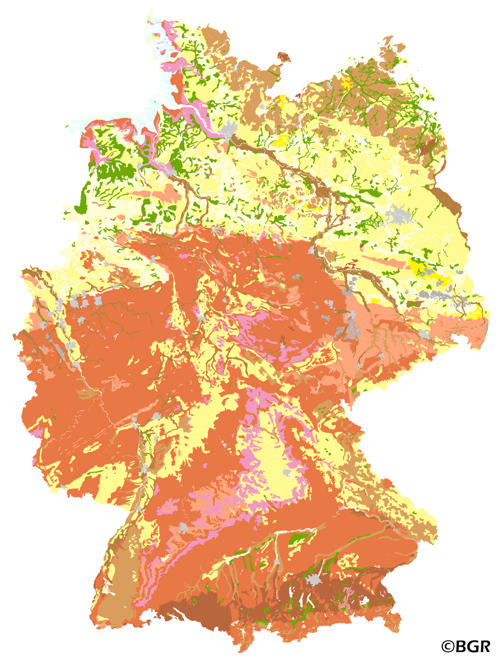
The map shows the distribution of typical soil types (soil texture) in the topsoils of Germany. Typical is used in the term of areally dominating. The map visualizes the results of the project that are documented in a BGR report (Bodenarten der Böden Deutschlands; BGR Archiv, Nr. 0127305). The soil texture data from the analysis of the particle size distribution for 16,132 sites in Germany were classified after the legend units of land use-stratified soil map of Germany 1: 1,000,000 (BÜK1000N V2.3) and mean soil texture were calculated. Considering the large heterogeneity in the data and the resulting uncertaintly in the precision for a site the depiction of the obtained soil texture is presented at the level of the soil types group, according to the German soil classification system (KA5).
-
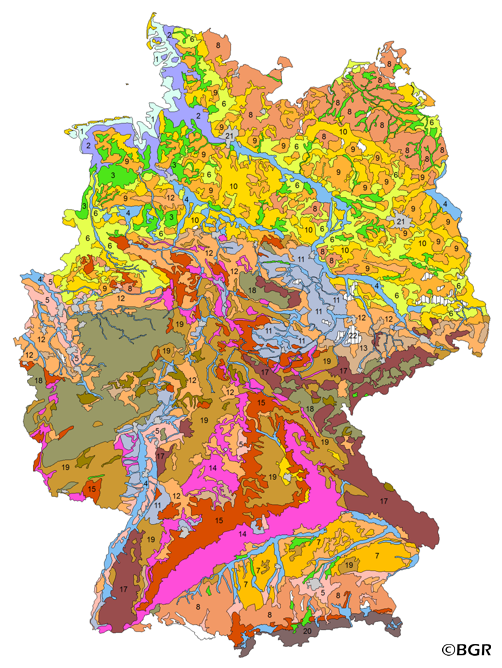
The BUEK5000 is derived form the landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 by aggregation, focused on information about the parent material, and generalization. The maps shows 20 soil (23) legend units with polygons of at least 64 square kilometers.
-
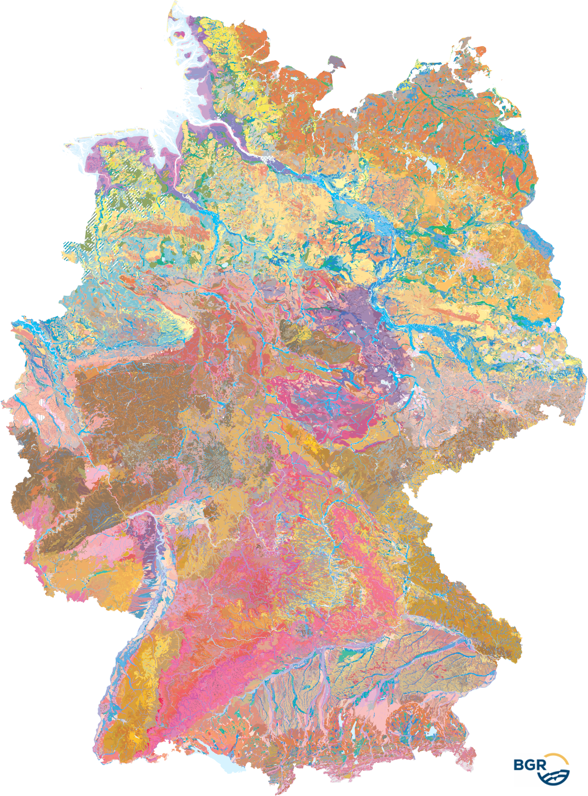
The Soil Map 1:250,000 (BUEK250), the digital successor to the Soil Map 1:200,000 (BUEK200), provides a detailed, nationwide standardized and comprehensive information basis for cross-state statements on soil use and soil protection in Germany. The present graphic dataset, version 6.0, is essentially based on the BUEK200, which was developed by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) in cooperation with the State Geological Surveys (SGD) of the federal states. It is graphically free of sheet sections and describes the distribution and association of soils on the basis of a total of 2171 legend units. The detailed pedological information is stored separately in a relational database and can be linked to the BUEK250 graphic dataset via the GEN_ID data field.
 INSPIRE-1
INSPIRE-1